What Goods And Services Do You Think Different Levels Of Government Provide Citizens?
If you've tuned into the news lately, you've seen the checks and balances system of government at piece of work. Whether it's courts hitting down executive orders or governors vetoing legislation, checks and balances are constantly working to keep the United States government functioning. But what are checks and balances, exactly? And how do they aid make democracy work? Although it's important for everyone to understand the checks and balances system, it'southward peculiarly disquisitional for y'all to understand if you're taking a government course. Additionally, since a system of checks and balances plays an essential role in the U.S. federal regime, the concept will also be a heavy contender for an AP exam costless response question. That'due south a lot to cover, huh? Non to worry, though! By the end of this guide, you'll accept all the information you lot need to Let's become going! A arrangement of checks and balances places limitations and controls on the ability and responsibility of each branch of authorities. You probably already know that the U.s. government isn't the simply government in the world that depends on a system of checks and balances to office properly, just for our purposes, we're going to focus on how the arrangement of checks and balances functions in the U.s.a.' course of regime. To really understand why checks and balances are such a big deal in the United states government, we demand to first with the post-obit: Agreement the history and background of our checks and balances government will lay the foundation for a checks and balances definition that you lot can use on the AP examination. Ii key influences shaped the Founders' decision to build a system of checks and balances into the United States Constitution: The overbearing behavior of the English language monarchy inspired the xiii colonies to declare independence and influenced the Founders to form a government organisation that was built on the ideas of liberty and freedom. They wanted to form a government in the United States that guarded confronting the kind of overreach they'd witnessed in the English government. That's where the writings of Baron de Montesquieu came in. Montesquieu originated the political doctrine of separation of powers within a government. (Spoiler alert: checks and balances are the result of this thought!) In his The Spirit of the Laws, Montesquieu argued for a constitutional government comprised of 3 separate branches. And these separate branches, Montesquieu argued, should have specific abilities to check the powers of the other branches. In other words, Montesquieu imagined a balanced government where no one branch was more powerful than the other. Montesquieu's philosophy heavily influenced the writing of the U.S. Constitution and the Founders' establishment of the iii branches: the executive co-operative, the legislative branch, and the judicial branch. The Founding Fathers believed that implementing a system like this in the U.s. would help continue government power in check and allow citizens to take more liberty. The Founders' vision for a government that separated powers took the form of a ramble republic. A constitutional democracy is a political system in which the federal authorities gets its potency to govern from the people. (Actually, you tin can learn tons more than about it means to be a democracy in this article!) But in general, constitutional democracies similar the United States are designed to practice ii things. Outset, their primary job is to protect the primal rights of every citizen, regardless of economic status, race, or form. 2d, constitutional democracies limit the amount of authorities power through a series of limits established by the United States Constitution, which are more commonly referred to as "checks and balances." These checks and balances include things similar: So what's important for you to remember about this description of a constitutional democracy? The large takeaway is that the system of checks and balances was written into the U.S. Constitution because the Founders knew it would be essential to the proper functioning of the United states of america' class of authorities. But implementing a system of checks and balances doesn't stop with writing it into the Constitution--that's but the showtime. The Constitution holds the three branches of the U.S. federal government responsible for adhering to the arrangement of checks and balances. To add to your working checks and balances definition, nosotros'll explain the three branches of the federal regime and how they piece of work within the organisation of checks and balances next. Checks and balances can work in many different ways and hold varying levels of importance in a government that employs such a system. In the U.S. Constitution, the 3 branches of the federal government were designed to operate separately and independently, just to be equal. In other words, no single branch should have more than ability than either of the others. Hither's how the system of checks and balances works in practice in the United States : one branch is given the power to have a given action, and another co-operative (or branches) is given the responsibility to confirm the legality and appropriateness of that action. That'south just a fancy fashion of saying that every time one co-operative makes a decision, it'south the responsibility of the other branches to evaluate it. The system of checks and balances facilitates a reciprocal relationship betwixt the different branches of the U.S. federal authorities. The three branches need each other—under the Constitution, the federal government couldn't fulfill its duties to the people without the proper function of each private co-operative. To understand how the iii individual branches piece of work independently and together in a arrangement of checks and balances, let's ascertain and examine each branch side by side. The U.Southward. Capitol building The legislative branch of the federal government is established by Article One of the Constitution and is known equally the United States Congress. Congress is in charge of creating laws and is made upward of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The legislative branch is big: at that place are 100 members of the Senate, chosen Senators, and 435 members of the House of Representatives, called U.Due south. Representatives or Congresspersons. As the biggest branch of the federal government, Congress has a lot of responsibilities, which include: You might be gathering from the list of responsibilities above that the legislative branch's overarching responsibleness is creating, providing for, and decision-making: they draft laws, pass bills, make rules, declare things, and make sure that the other branches are following the rules. In other words, they legislate. The U.Southward. White Business firm The executive branch of the federal government is established past Article Two of the Constitution and is made up of the president, the vice president, the Chiffonier, executive departments, contained agencies, and other boards, commissions, and committees. When nosotros hear the discussion "executive," a powerful individual in a well-tailored adapt might popular into our minds. Just considering the President of the United States is the head of the executive branch doesn't hateful they're a lone wolf, though. All of the other members of the executive branch back up and advise the president, and actually do a lot of the work in the executive branch. The Cabinet is comprised of the vice president and the heads of the 15 executive departments. These department heads accept titles like "secretary," "director," or "ambassador," and they're in charge of everything from the Department of Homeland Security, to the Department of Transportation, to the Section of Pedagogy. For example, the Secretary of Land and the Secretary of the Treasury are both heads of their respective departments and members of the president's Chiffonier. The Secretary of Land advises the president on foreign diplomacy, and the Secretary of the Treasury advises the president on economic diplomacy. The Cabinet may also be asked to advise the president on responsibilities or decisions that pertain to executive checks on the other two branches, or the executive branch'southward response to checks initiated past the other two branches on the executive branch. This is ane key mode that the president receives both support and accountability in carrying out the duties of the executive branch. Now that you know who makes up the executive co-operative, allow's look at the executive branch's key responsibilities: Y'all're probably gathering from this list that the executive branch'southward main role is to implement and enforce federal laws. It's chosen the "executive" branch for a reason, right? The executive branch executes: it makes sure that the right stuff gets washed. Information technology puts plans into action and carries out different laws and orders. The U.S. Supreme Court building The judicial branch is established by Article 3 of the Constitution, and information technology'southward the judicial branch'due south chore to evaluate, translate, and apply laws. The judicial branch is made up of iii dissimilar courts: the Supreme Courtroom, the Appellate Courts, and the District Courts. Allow's await at what each of the three courts within the judicial branch tin can do. The Supreme Courtroom is the highest federal court in the U.s.a. and is the head of the judicial branch. It's made up of one Primary Justice and viii Associate Justices. Appointments to the Supreme Court are made for life, so when the President nominates justices and the Senate approves them, information technology's a really large deal. The Appellate Courts--also called courts of appeals--are the intermediate courts of the U.S. federal courtroom system. There are thirteen of them, and they serve as a sort of go-between for the Supreme Court and the more than numerous District Courts. The Appellate Courts hear appeals from the District Courts and, when appropriate, appeals court decisions to the Supreme Courtroom. The District Courts are the terminal component of the judicial branch. The Commune Courts are where federal trials happen, which is a big responsibleness, as there are 94 juridical districts in the U.s.a.. Their jurisdiction covers both civil and criminal federal cases. Now that you know well-nigh the dissimilar courts that make up the judicial branch, hither are the primary responsibilities of the judicial branch: You can probably tell from the language used in the list of responsibilities above that the Judicial branch'southward primary responsibility is dealing with interpretation : the Judicial branch interprets laws, policies, cases, testimony and evidence through the Constitution. The system of checks and balances works like gears in a machine. It takes the work of all three branches of regime in unison to keep the land running. Now you know about the three branches of government: who the key players are, what they do, and why they practice it. Examining the checks and balances that are assigned to each private branch is the next pace to getting you better acquainted with how each co-operative works. When nosotros described the responsibilities of each co-operative in the previous sections, nosotros were simultaneously describing how they check the other branches of the federal government. But we think it might be easier to envision how those responsibilities role explicitly equally checks and balances if we place them side by side in a tabular array. If you lot're a visual learner, this is for you! Looking at all of the checks and balances in one identify can too help yous call back critically about the reciprocal human relationship between the different branches and the specific ways that they work together on different topics, issues, and areas of the federal government. To give you lot a better thought of how the branches work together to bank check each other, we've laid out the different checks and balances in a tabular array below. Each row explains how the branches of government cheque and balance each other effectually a specific topic. Permit's take a look: Legislative Co-operative Powers Executive Co-operative Powers Judicial Co-operative Powers Creating Laws Strange Treaties Implementing and Interpreting Laws Official Role Appointments War Appointing Judges and Justices Executive Co-operative Deportment Whew! That's a lot of checks and balances and political jargon. Allow'southward make sense of all this info by identifying some pros and cons of how the powers and responsibilities are distributed in the U.S.'s version of the arrangement of checks and balances. Now you lot have a visual for how checks and balances are assigned and distributed among the three unlike branches of the U.S. federal regime. But what does this all hateful? First, it's important to recognize that the unlike branches of the federal government aren't in some kind of combative relationship considering of the system of checks and balances. They don't act like rival sports teams (usually)! Instead, the powers and responsibilities assigned to each co-operative were intricately coordinated by the writers of the Constitution so the government would operate collectively in the best involvement of the people. Only it'due south a fact of political life that no government system is perfect in practice. On the AP exam, yous might exist asked to explain or analyze an case in which the organisation of checks and balances didn't exercise its task, or perhaps to analyze a situation when the arrangement of checks and balances worked to the advantage of U.Southward. citizens. In order to do this, you'll demand to understand some of the pros and cons of the U.South.'s checks and balances organization so you can requite a stellar checks and balances definition and analyze and explain checks and balances examples on your own. Check out our list of v pros and cons of checks and balances below to assistance grow your understanding of how the system can work in action. Nosotros're bringing this ane upwards again considering information technology's the primary concept behind implementation of a system of checks and balances: checks and balances guard against tyranny and abuse of power by preventing an individual or pocket-size group within the government from seizing also much ability. We encounter this exemplified all-time in the relationship between the legislative, executive, and judicial branches where creating and passing laws is concerned. The legislative branch can propose bills or laws, the executive co-operative can veto them, the legislative co-operative can override the executive veto through a 2-thirds vote, and the judicial branch tin can declare laws unconstitutional. In the procedure of passing legislation, and then, no one private or co-operative can catch an undue corporeality of ability, and that'due south one of the things that the organization of checks and balances does best. It distributes ability every bit evenly equally it can among the different branches of the government. What'due south key in thinking almost checks and balances every bit an of import way to forbid tyranny is that they make the government to check itself and limit its own influence. Though information technology isn't fun to think about the possibility of our government becoming tyrannical, the organisation of checks and balances prevents any cocky-interested minority within the government from grabbing too much ability and acting merely in the interests of its group. On the flip side, smaller factions or groups in the minority within the government are always going to keep a close eye on the grouping that's in the bulk. They'll be eager to make sure the bulk group aren't getting upward to any funny business. If there are corrupt practices going on in the majority, the minority groups in the regime will certainly phone call those out. Political parties are a classic case of how cocky-regulation can occur in the government. For example, when the Republican political party holds the majority in the Business firm or the Senate, the Democrats in the House and the Senate are extra vigilant nearly keeping the Republican bulk in check. Loyalty to political parties presents enough of challenges to the system of checks and balances, just the inherent competition betwixt the different political parties represented within the legislative branch can often serve to bank check the power of self-interested groups. Checks and balances enable the three branches of government to disagree. In a organisation that separates power among unlike institutions comprised of many different people, multiple minds work to interpret the Constitution. And when multiple minds are doing that interpreting, disagreements about what is and is not constitutional tin ascend. That might seem antagonistic and counterproductive to getting things done in the authorities, merely the ability for the different branches to disagree is in the interest of the liberty of the people. When the different branches of the regime accept the opportunity to work through disagreements most diverse decisions that impact the people, decisions are made more deliberatively. And the government has the power to make huge decisions, and so the slower pace of decision-making enabled past the system of checks and balances can help ensure that these decisions are the all-time ones. The flip side of constitutional support for disagreements amongst the different branches is that policymaking tin can be much more than time consuming. One branch can propose a police force, another can veto information technology, and another can say that that constabulary violates the Constitution, and and then on. Sometimes the iii branches won't agree and a stalemate will ensue . . . meaning no policy changes occur, or they're put off for a long time. This tin can be a skillful thing in some cases, peculiarly when there is a majority in the House and the Senate who but have the interests of one political party or credo in mind in policymaking. Merely sometimes the people want change, and the main matter standing in the way of changes occurring is the different branches' uses of the system of checks and balances. Interpreting the Constitution has proven tricky equally the United States has grown and changed. For case, the writers of the Constitution couldn't have predicted the United States' massively expanding population, the technological revolution, or global conflicts like World War I and World State of war 2.. All of these changes bear on the way the Constitution is interpreted--which includes how checks and balances are understood and implemented. This has led to internal conflicts within the 3 branches of government. In that location have been points in history where different branches take tried to expand their power beyond what was originally outlined in the Constitution, and sometimes, the branches accept succeeded. For example, to defend the U.S. and its economy against fascist strange powers, President Franklin D. Roosevelt's New Bargain restructured the federal government and greatly expanded executive powers. So why is this a "con," exactly? Remember: the system of checks and balances exists to make sure that no one branch of regime is stronger than the other. When 1 branch tries to expand its power, it runs the risk of throwing the "balance" part of the "checks and balances" procedure out of equilibrium. That opens up a chance for an overreach of ability, which can potentially put citizens' freedoms at risk. Former President Beak Clinton, who was the President of the United States from 1993–2001 To really hone your agreement of checks and balances, examples are essential! Checks and balances can play out in interesting means in existent-life situations, and then we're going to summarize and break down one example for you lot to reference here. The example we're going to look at is the Line Item Veto Deed of 1996 , which led to a Supreme Court case involving President Bill Clinton in 1998. This example is kind of a doozy—the checks and balances enacted past all three branches in this situation played out over a decade . . . and the Line Particular Veto Deed yet failed to win approval in Congress and become police. Allow's get into the details of the Act and the example and see what it tin teach us about checks and balances. The Line Item Veto Act of 1996 immune the president—Neb Clinton, at that fourth dimension—to veto parts of bills selectively, rather than vetoing bills in their entirety. The main purpose of this Act was to give the president more than control over the details of the federal budget--a ability that was constitutionally reserved for Congress. Congress successfully passed this legislation in 1996. How did that happen? Well, in the federal midterm elections of 1994, Republicans took over the House and the Senate from Democrats. This was seen as a pretty big upheaval. It'southward fifty-fifty been called the "Republican Revolution!" The Republicans also succeeded in taking the majority in Congress by making a pretty hefty campaign hope to the American people in the form of the "Contract with America." The Contract with America was basically a long list of actions the Republican candidates promised to take if they gained control of Congress. The Line Item Veto Act was a key piece of the Contract with America. The American people liked this Act because it promised to ensure congressional fiscal conservatism. In fact, they had that in mutual with then-President Clinton: the only provision in the Contract with America that he was willing to support was the Line Item Veto Human action. Since Republicans controlled Congress, and since the president supported the Line Particular Veto Deed, it passed both the legislative and executive branches without existence vetoed or rejected. And then things started to get a fleck ugly. In the fourth dimension that the Line Particular Veto Deed was law, President Clinton did a lot of line item vetoing. In fact, he applied the line-item veto to the federal budget 82 times. Does that sound like a lot? It did to the people who were affected past the president'southward line-item vetoes, and that'southward where the checks and balances started coming into play. When the Human activity was passed in 1996, lots of Democrats broke with President Clinton to oppose it. A congressman even sued to prevent employ of the line-detail veto. At the time, the Supreme Court held that the congressman's instance lacked standing because he couldn't give whatever specific examples of how the Line Item Veto Act was causing harm to people. Only when President Clinton began using the line-item veto a little more than liberally, more than people filed suit. Since Clinton was making ample use of his new power, this time, the plaintiffs had specific examples of how the line-item veto was causing harm. The Urban center of New York itself and several other healthcare organizations declared financial injury from President Clinton'due south counterfoil of various provisions from Acts that were passed in 1997. The case—Clinton v. Metropolis of New York—went earlier the District Court, and the Court ruled in favor of the plaintiffs. This time, the Court held that the Line Detail Veto Act was unconstitutional. The Commune Courtroom then used its power to appeal to the Supreme Court. The case was headed to the highest federal court in the U.s.a.. In 1998, the Supreme Court ultimately ruled that the Line Item Veto Act violated the Presentment Clause of the Constitution, which outlines a specific do for enacting a statute that the Act did not follow. The Supreme Courtroom used their power of interpretation to rule that the Constitution expressly prohibited the actions that the Act enabled the President to take. The majority of the Supreme Courtroom, in other words, believed that the Human activity violated principles of the separation of powers and threatened private freedom past giving the President the ability to reward or favor certain groups and punish others. Former President George W. Bush, who was President of the United states of america from 2001–2009 In 2006, the Line Particular Veto Act came up over again. That year, President George West. Bush asked Congress to enact legislation that would return the line item veto power to the executive branch, and announced his intent to brand this request in his Land of the Union Address. In March 2006, President Bush sent a legislative proposal to Congress and urged its prompt passage. Anticipating dissent from some members of Congress and the Supreme Court, members of President Bush's Chiffonier argued that his version of the Act was different from the Line Particular Veto of Deed of 1996 because the new proposal would seek congressional approving of all line-item vetoes, instead of giving the executive unilateral say-so for such vetoes. Many members of Congress didn't purchase this argument. Some however believed that the legislation would take away parts of Congress'southward constitutional power and give it to the executive branch instead. After hearing arguments from ramble law experts about the constitutionality of the nib, the House Budget Committee approved the proposed Human action through a bulk vote. The full House of Representatives voted and approved the same bill soon afterwards, but it failed to win approval in the Senate. But because the Human action didn't win total approval past Congress, the Legislative Line Particular Veto Act of 2006 didn't become law. If you lot were paying attending, you may have picked out some of the checks and balances that were involved in the whole scenario surrounding the Line Item Veto Deed. To help y'all out, here's a list of the checks and balances that we found playing a office in this legislation: The Line-Item Veto Act of 1996 is a bang-up example of how we can understand the federal government'south powers as being both divided and shared. In some aspects of this case, branches used their powers to work together to keep another co-operative from doing something that was not constitutional and that potentially threatened the liberty of the people. By checking each other in this case, the different branches as well dedicated their own constitutional powers by preventing the executive branch from challenge powers that the Constitution assigned to the legislative branch. This example shows how existent-globe cases of checks and balances in activity have a lot of layers: there's a lot to clarify and unpack, and sometimes who'south right and who's incorrect isn't easily defined. That's why information technology's important to expect at both the big picture state of affairs and all of the details, which is key to making sense of checks and balances in activeness! This is merely an overview of how checks and balances work within the U.s.a. regime. (We know...it's a lot!) In that location's a lot more to larn about how each individual branch checks the other. A adept place to get-go is learning more near how the Executive co-operative checks the Judicial branch. The AP U.S. Government examination is virtually more than than merely how the federal government works, though. That's why nosotros've adult the all-time 5-step guide to help you prepare. In one case y'all've worked your way through that, it's time to drill deeper into the fabric you need to know to ace the exam. Hither'due south a list of the best AP U.South. Government notes on the cyberspace, and here's a step-by-stride guide to acing the AP U.S. Government'due south FRQs.

What Are Checks and Balances? Definition and History
Where the Thought of Checks and Balances Comes From

A Ramble Democracy: The Vehicle for a Organisation of Checks and Balances
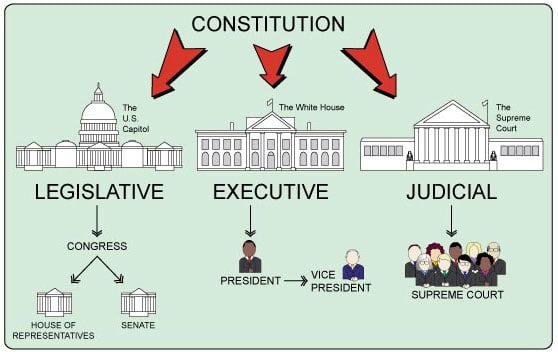
The 3 Branches of the United States Federal Authorities

The Legislative Branch

The Executive Branch, Defined

The Judicial Branch, Defined
The Supreme Courtroom
The Appellate Courts
The District Courts
The Judicial Co-operative'southward Responsibilities

How Does the Checks and Balances Organisation Work in the United States?
Checks and Balances of the 3 Branches of Regime

v Pros and Cons of a Checks and Balances Organisation
Pro: They Keep a Unmarried Group From Grabbing as well Much Power
Pro: They Go the Government to Self-Regulate
Pro: They Provide Ramble Support for Disagreements Betwixt the Branches
Con: They Can Complicate Policymaking
Con: The Organisation Doesn't Always Piece of work as Originally Intended

What Are Checks and Balances Like in Action?
The Line Item Veto Act of 1996: Groundwork
The Judicial Co-operative Acts

The Legislative Branch Acts
Summary of the 4 Checks and Balances Involved in This Instance

What's Next?

About the Author
Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English language Literature. As a content author for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving higher-bound students the in-depth information they demand to get into the schoolhouse of their dreams.
Source: https://blog.prepscholar.com/checks-and-balances-definition-examples
Posted by: begayeelbectern.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Goods And Services Do You Think Different Levels Of Government Provide Citizens?"
Post a Comment